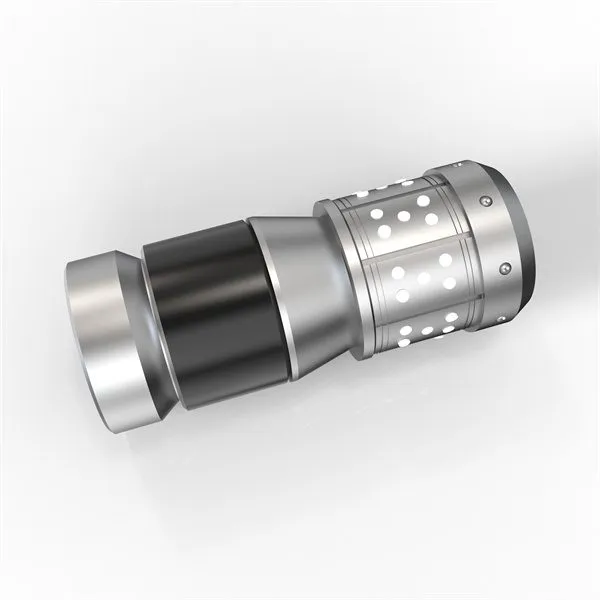
Mud Valve
Silent Guardian in Industrial Fluid Control

Peças para campos petrolíferos
Amid the roaring mechanical sounds of oil drilling platforms, in the winding pipeline network of mine dressing plants, and in the intricate treatment systems of sewage treatment plants, a special type of valve is silently guarding the safe operation of industrial processes. This device, called mud valve, rarely enters the public eye, but plays an indispensable role in the modern industrial system. This article will deeply analyze the technical characteristics, application scenarios and development trends of this key equipment, revealing its unique value in the process of industrial civilization.
Equipamento de cabeça de poço
- Technological evolution: from cast iron valves to intelligent control
The evolution of mud valves can be regarded as a microcosm of the industrial material revolution. In the late 19th century, the first generation of mud valves made of cast iron emerged in mining, and its rough sealing surface required workers to manually clean the scale regularly. In the 1920s, with the breakthrough of stainless steel smelting technology, 316L austenitic stainless steel valves began to be used in acid mine drainage systems, and the corrosion resistance was improved by more than 3 times. Entering the 21st century, the application of tungsten carbide coating has made a qualitative leap in the wear resistance of the valve seat. With the hydraulic drive system, the service life of a single valve has exceeded 100,000 opening and closing cycles.
In the field of structural design, mud valves have undergone three major innovations. The early gate-type structure was limited to a working pressure of 0.5MPa and was gradually replaced by a plug valve with a self-cleaning function. The birth of the modern eccentric hemispherical valve, through a unique 45° deflection axis design, enables the valve core and the valve seat to form a shear motion, effectively solving the problem of viscous medium blocking. The newly developed intelligent regulating valve integrates a pressure sensor and a microprocessor, which can automatically adjust the opening angle according to the viscosity of the medium, reducing energy consumption by up to 18%.
Válvula
- Core function analysis: Beyond simple opening and closing
The technical characteristics of the mud valve are concentrated in its unique design for dealing with complex working conditions. The valve body flow channel adopts a full-diameter structure, and the flow resistance coefficient is controlled below 0.08 to ensure the smooth passage of heavy media with a solid content of 60%. The double hard seal system consists of a Stellite alloy sealing ring and a ceramic coated valve core, which can maintain zero leakage under a pressure difference of 4MPa. In response to the special needs of deep-sea drilling platforms, the pressure-resistant shell design adopts finite element topology optimization, and the wall thickness is precisely controlled within the tolerance range of ±0.5mm, successfully passing the 15000psi (about 103MPa) pressure test.
In terms of adaptability to extreme working conditions, the low-temperature mud valve used in the Arctic oil and gas fields still maintains the elastic modulus stability of the sealing material in a -65℃ environment. The valves equipped in high-temperature oil wells in the equatorial region adopt a double-layer heat dissipation structure to reduce the surface temperature of the valve body from 320℃ to a safe range. These technological innovations have reduced the equipment failure rate from 3‰ of traditional valves to below 0.5‰.
- In-depth expansion of application scenarios
In the field of shale gas extraction, mud valves, as the core components of the fracturing fluid control system, need to cope with the flow impact of 20 cubic meters per minute. Field data from a North American shale block showed that mud valves equipped with a dynamic balancing system reduced the water hammer effect by 72%, significantly extending the life of the pipeline system. The fully electronically controlled mud valve used on deep-sea drilling platforms achieves precise control at a water depth of 3,000 meters through optical fiber signal transmission.
Gate Valve / (API 6A Gate Valve)
New applications in the field of environmental protection highlight the value of technological innovation. The intelligent sludge regulating valve developed by a German company integrates an online concentration detection module, which can automatically adjust the opening according to the solid content of the sludge, reducing the energy consumption of the dehydration system by 23%. In the lithium ore extraction process, the alkali-resistant mud valve uses Hastelloy C276 material, which successfully resists the corrosion of strong alkaline slurry with a pH value of 13.5, and the equipment replacement cycle is extended from 3 months to 2 years.
IV. Future Technology Atlas
Breakthroughs in materials science are reshaping the industry landscape. Graphene-enhanced polytetrafluoroethylene sealing materials show amazing wear resistance. Laboratory data show that its wear rate is only 1/8 of that of traditional materials. The topologically optimized valve body manufactured by 3D printing technology achieves a 40% weight reduction while maintaining the same strength. The introduction of digital twin technology makes it possible to manage the entire life cycle of valves. A pilot project reduced preventive maintenance costs by 35% through real-time stress field simulation.
The path of intelligent development is becoming increasingly clear. The valve health monitoring system based on the industrial Internet of Things can predict bearing failures 72 hours in advance through vibration spectrum analysis. The application of edge computing technology enables valves to independently determine the characteristics of the medium and adjust the control parameters. A pilot project showed that the intelligent adjustment system reduced the energy consumption of the grinding process in the beneficiation plant by 12% and increased the production capacity by 8%.
Conclusion
From the rough cast iron valves in the steam age to the data terminals in the intelligent age, the evolution of mud valves reflects the wisdom of human industrial civilization. Driven by the goal of carbon neutrality, the new generation of mud valves is rapidly evolving in the three directions of energy efficiency optimization, material revolution, and intelligent control. This silent industrial guardian will continue to write its own technical legend in the journey of human exploration of underground resources and protection of the ecological environment.